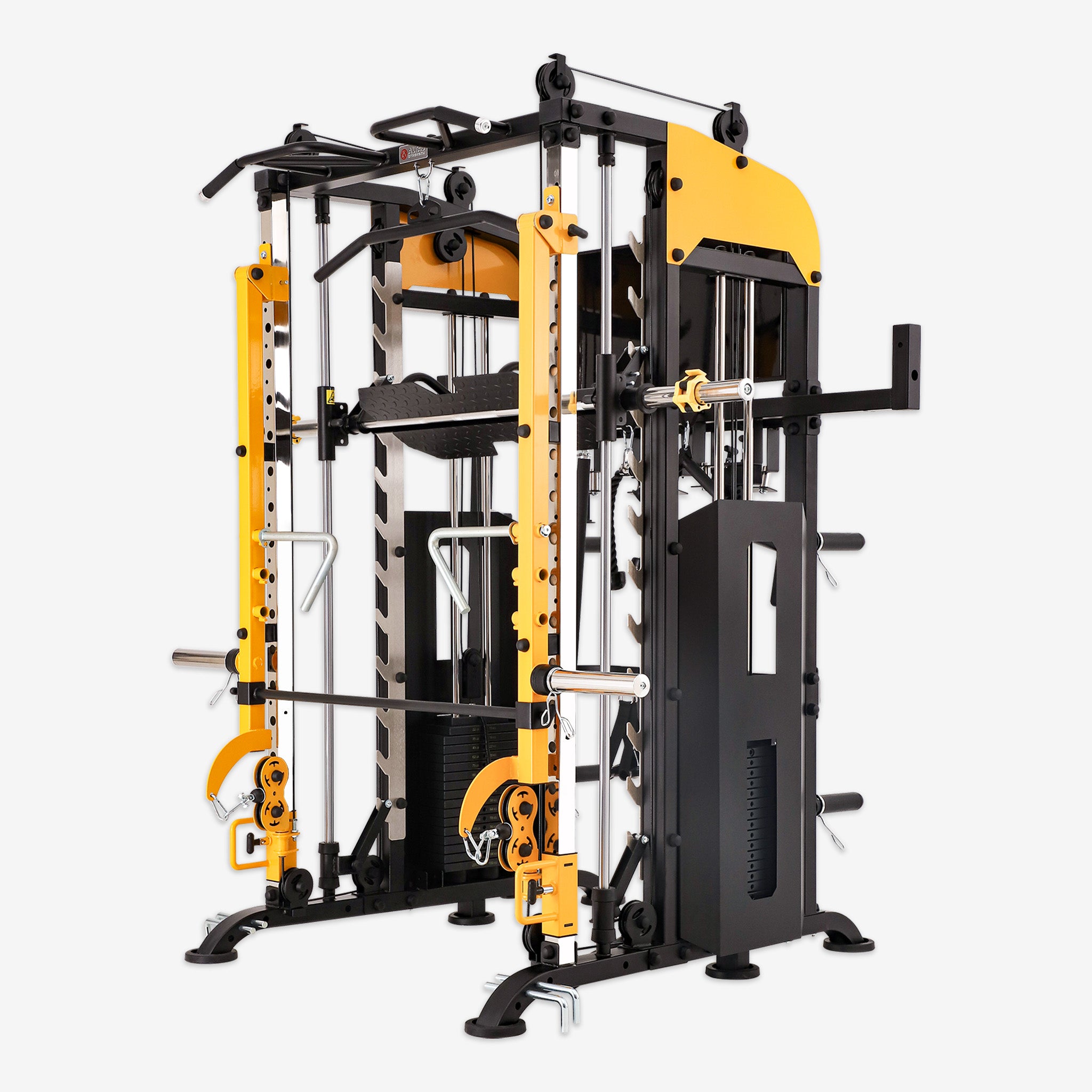
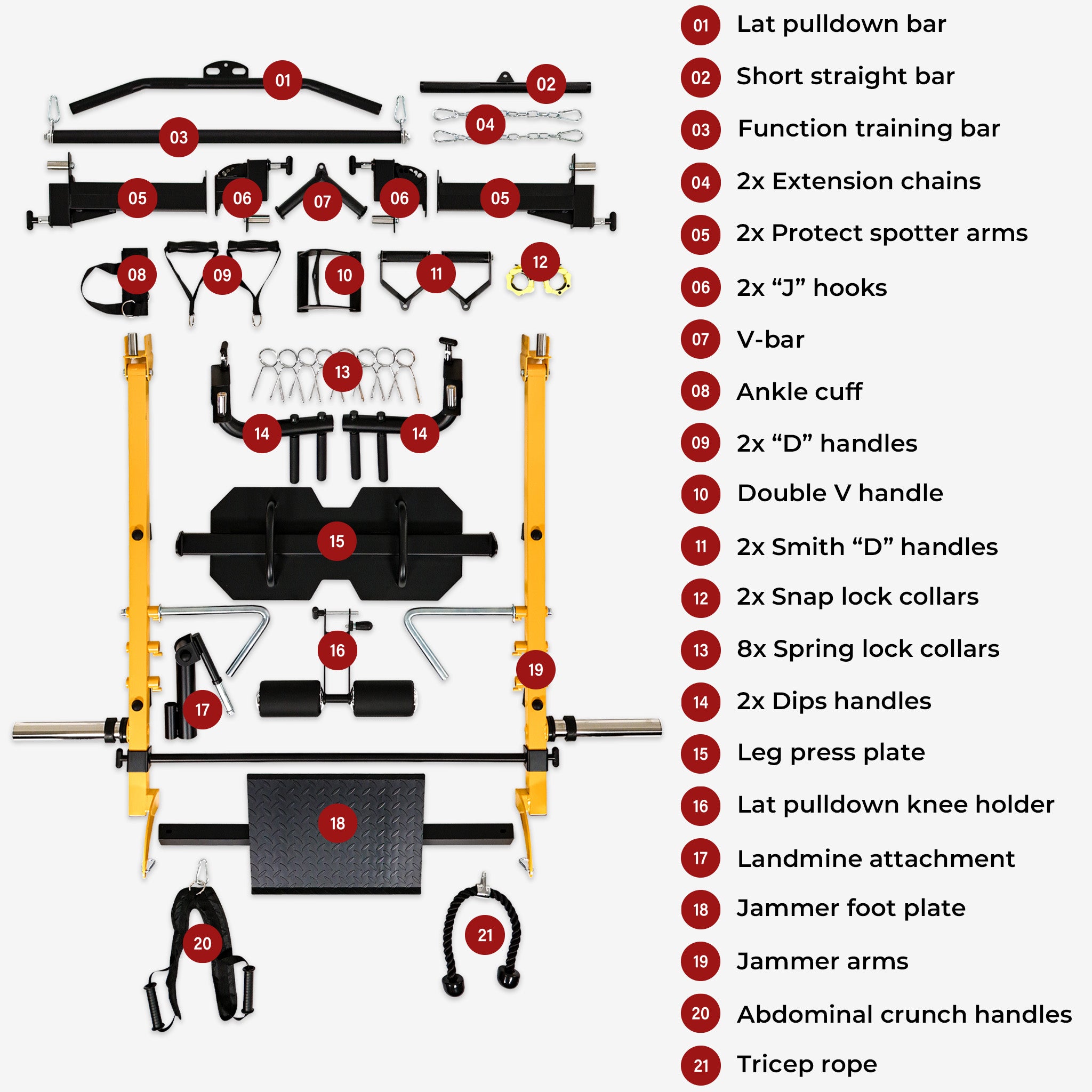
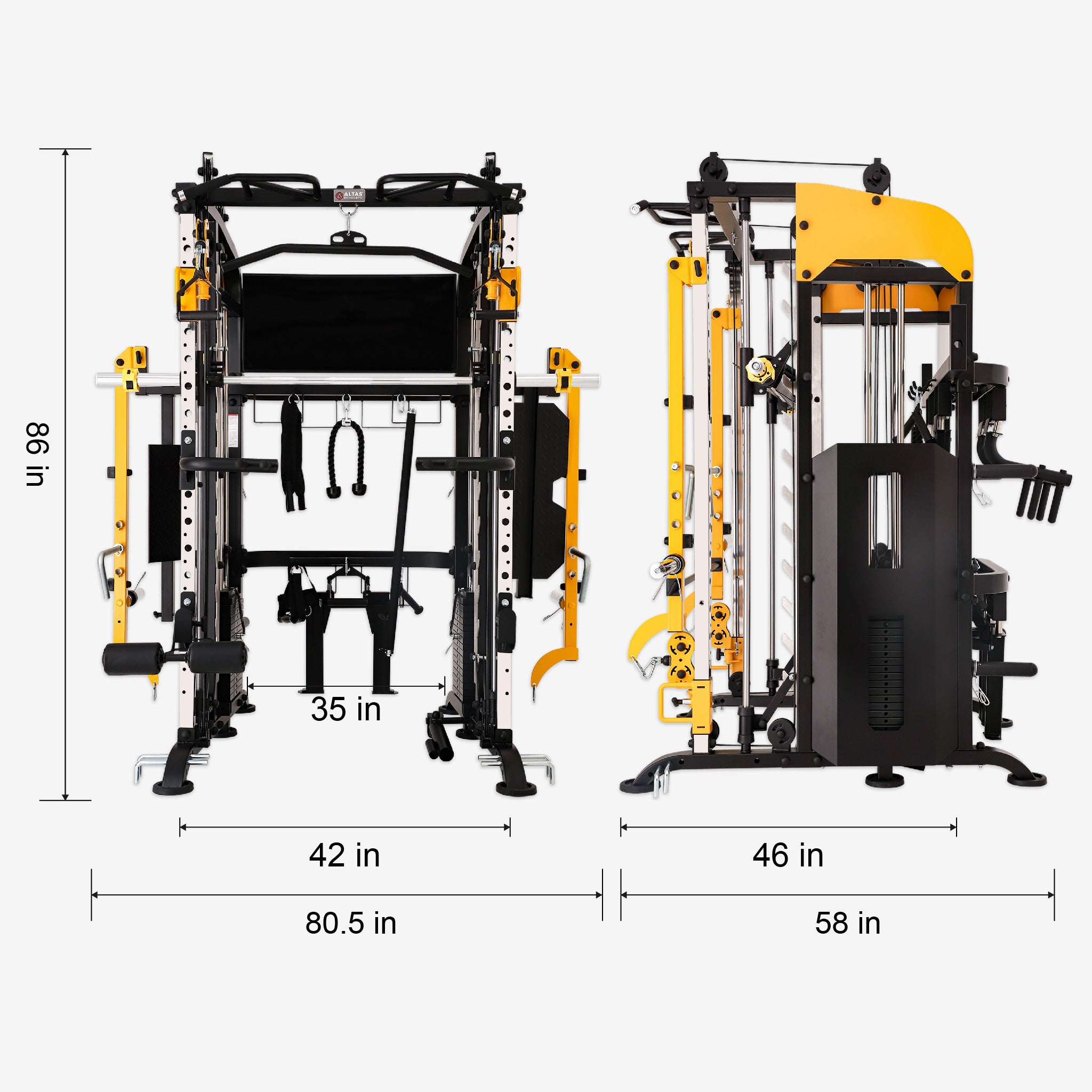
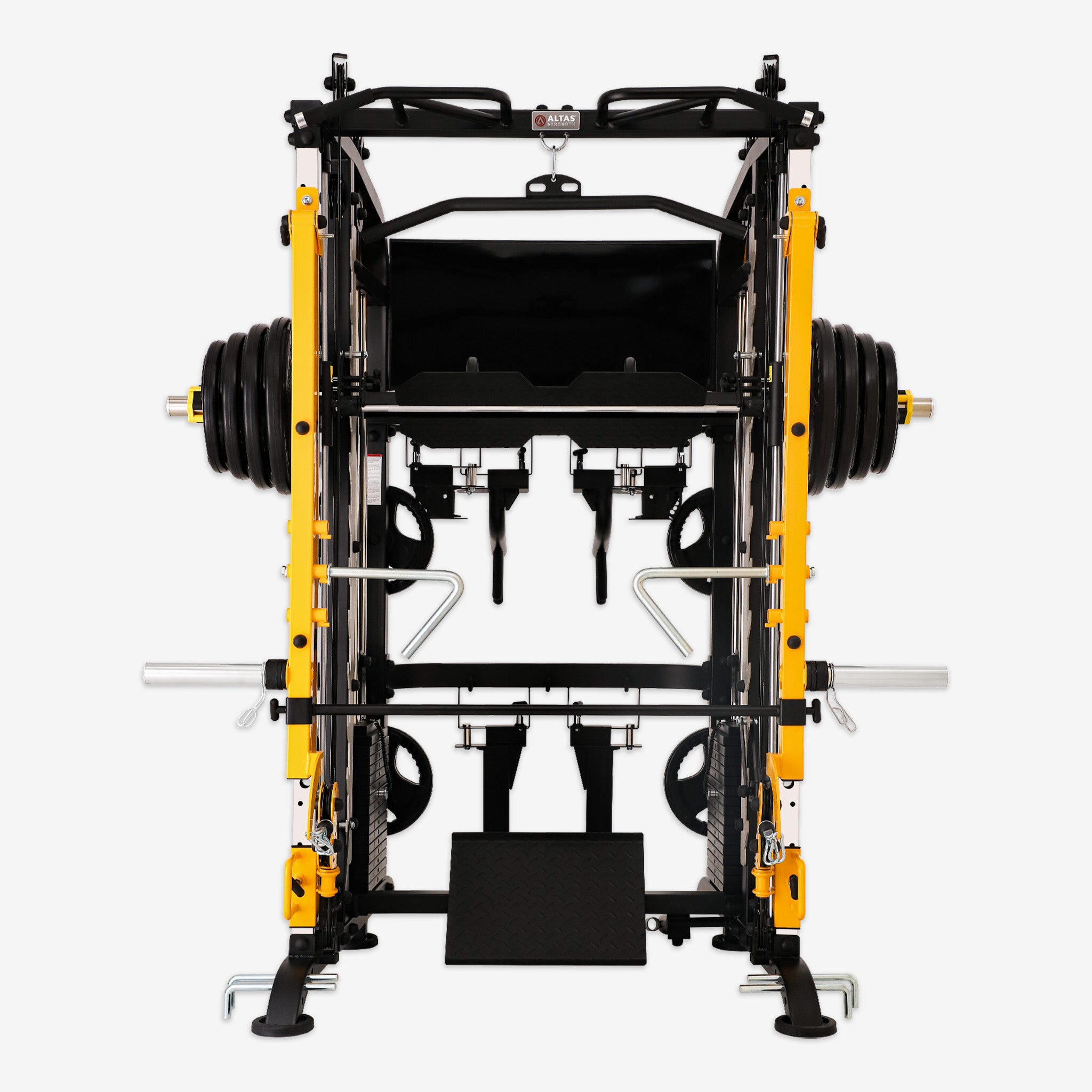
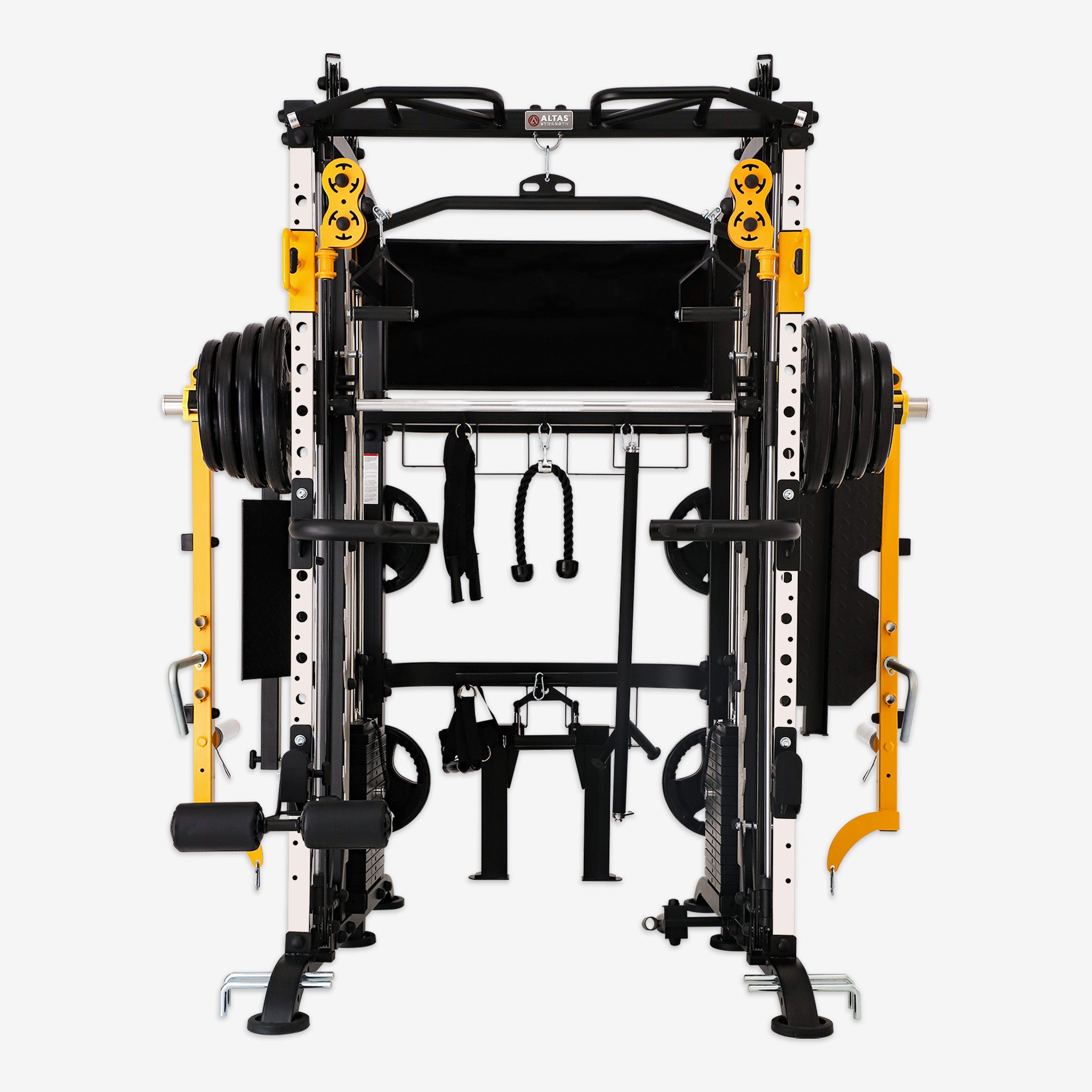
Muscle training, also known as strength or weight training, uses resistance like weights, bands, or body weight to build strength and muscle mass. Beyond creating a sculpted physique, it delivers significant health benefits. Let's dive into the science, practical techniques, and overall impact of muscle training.
I. The Science Behind Muscle Training
Muscle Physiology and Training Goals
Muscles are made of different types of fibers: fast-twitch for strength and slow-twitch for endurance. Based on your goals—whether it's building strength, enhancing endurance, or sculpting the body—different training approaches can be applied.
Neural Adaptation and Muscle Coordination
Strength training enhances how muscles and nerves work together. This neuromuscular adaptation boosts performance in activities like weightlifting, sprinting, or sports.
Muscle Growth and Repair
Training causes small muscle fiber damage, which rebuilds stronger with proper recovery. Overtraining, however, can cause injury. A smart training plan combined with adequate rest is critical for muscle growth.
II. Practical Methods of Muscle Training
Free Weight Training
Exercises like squats, deadlifts, and bench presses engage multiple muscle groups and mirror real-life movement patterns, making them ideal for strength and muscle gains.
Machine Training
Machines offer controlled resistance and help beginners or those targeting specific muscles maintain good form while minimizing injury risks.
Core Stability Training
A strong core improves posture and athletic performance. Planks, Russian twists, and other core exercises enhance the strength and endurance of your abdominal and back muscles.
Progressive Overload
To see consistent progress, you must gradually increase training intensity by adding weight, reps, or sets. This challenges muscles and drives growth.
Sets and Rest
Following a routine of multiple sets (e.g., 3 sets of 10 reps) and allowing muscles to rest is essential for recovery and growth. Avoid training the same muscle group on back-to-back days.
III. Benefits of Muscle Training
-
Boosted Metabolism: More muscle increases resting calorie burn, aiding fat loss.
-
Stronger Bones: Resistance exercises promote bone density and prevent fractures.
-
Better Athletic Performance: Strong muscles enhance movement efficiency and reduce injury risk.
-
Mental Health: Training boosts self-esteem, lowers stress, and improves mood.
-
Anti-Aging Effects: Strength training combats age-related muscle loss and keeps you vital as you age.
IV. Key Considerations and Recommendations
-
Proper Form and Warm-Up: Always start with a proper warm-up and learn correct techniques to avoid injury.
-
Personalized Training Plan: Tailor your program to your fitness level, goals, and body needs.
-
Nutritional Support: A high-protein diet helps with muscle repair and growth.
-
Avoid Overtraining: Balance intensity and recovery to prevent fatigue and injuries.
Conclusion
Muscle training is more than just building a great physique—it's a foundation for better health, improved athletic performance, and a more confident life. Whether you’re aiming for strength, endurance, or aesthetics, a well-structured, science-based training plan will help you reach your full potential. Start your fitness journey with smart strategies and feel the transformation in strength, health, and self-confidence!