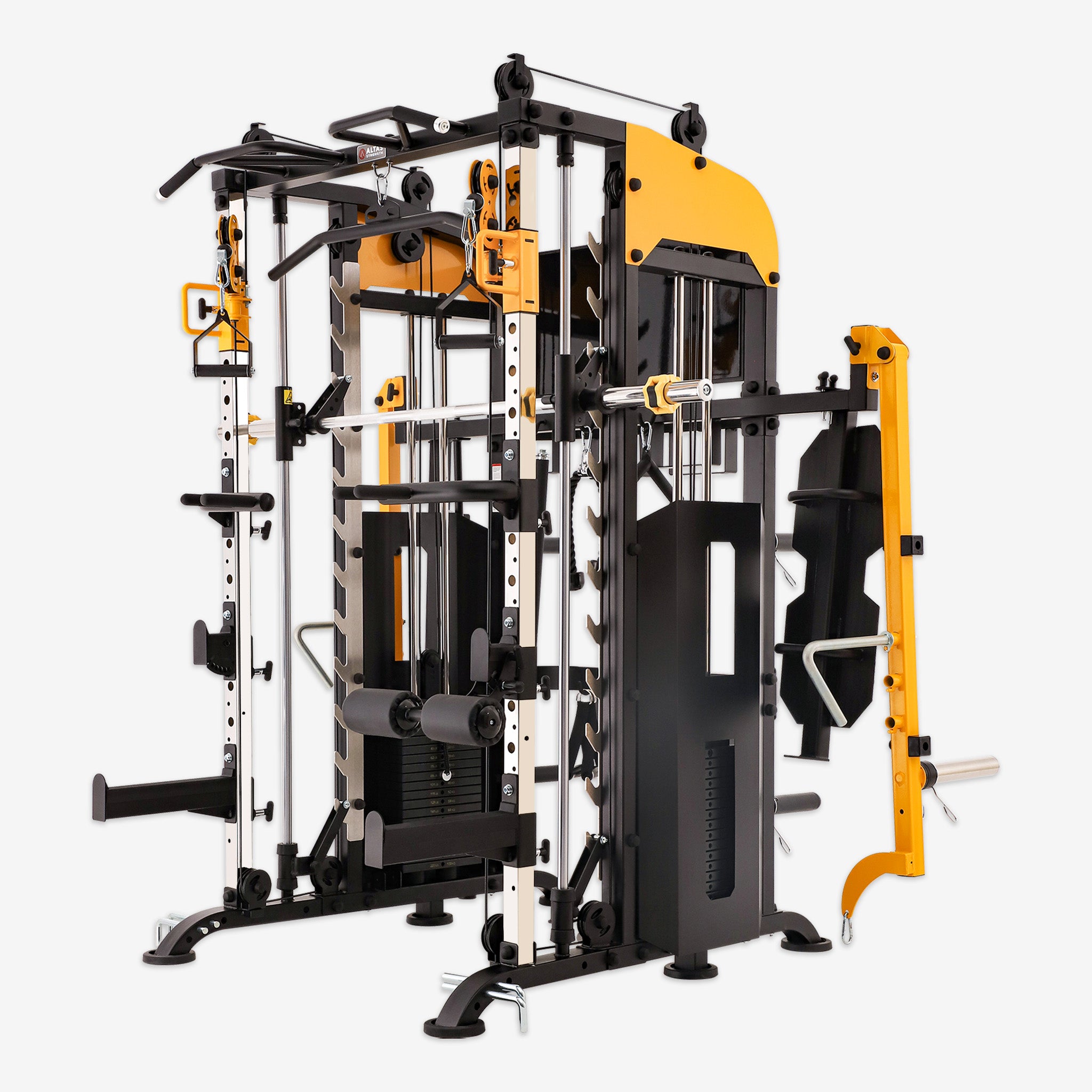
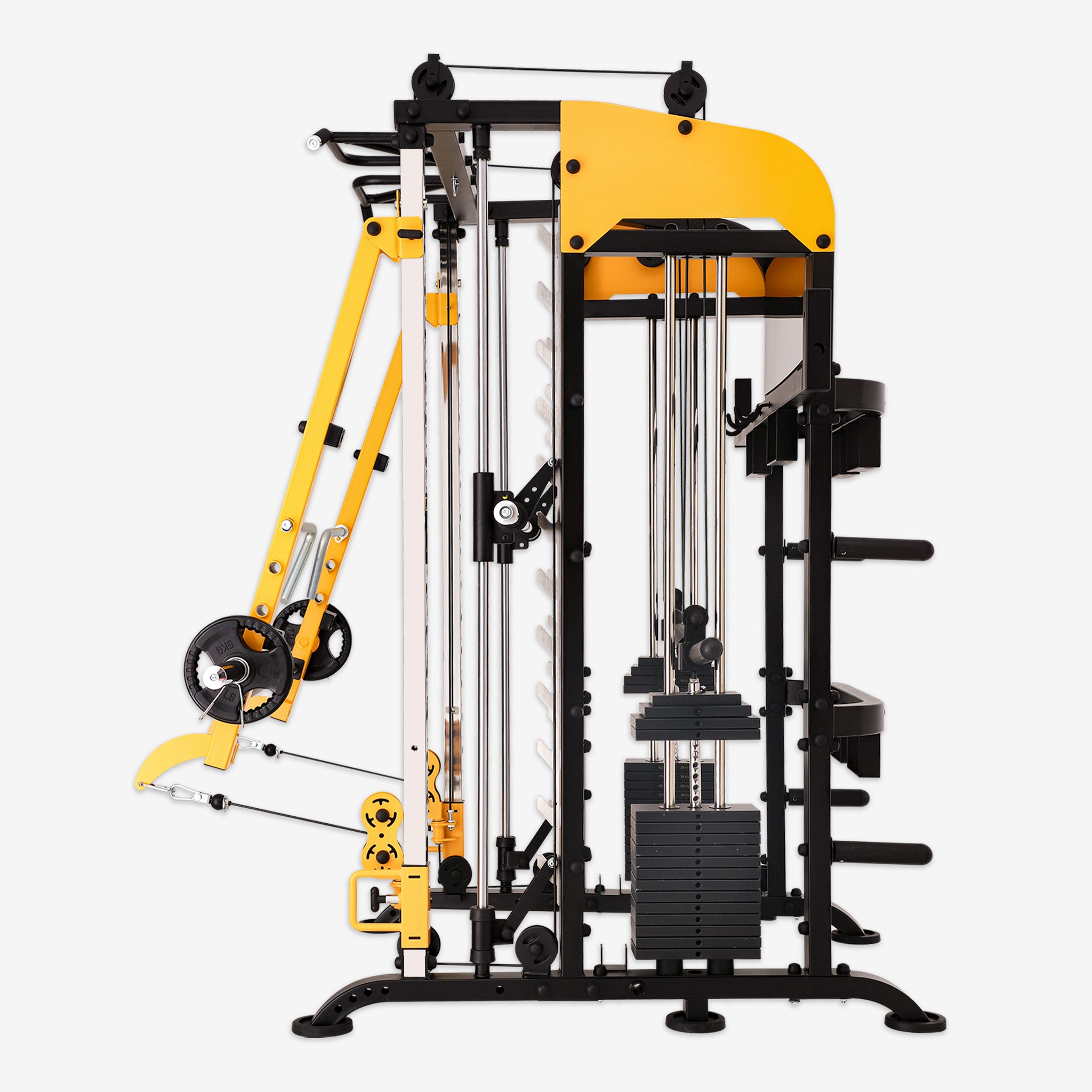
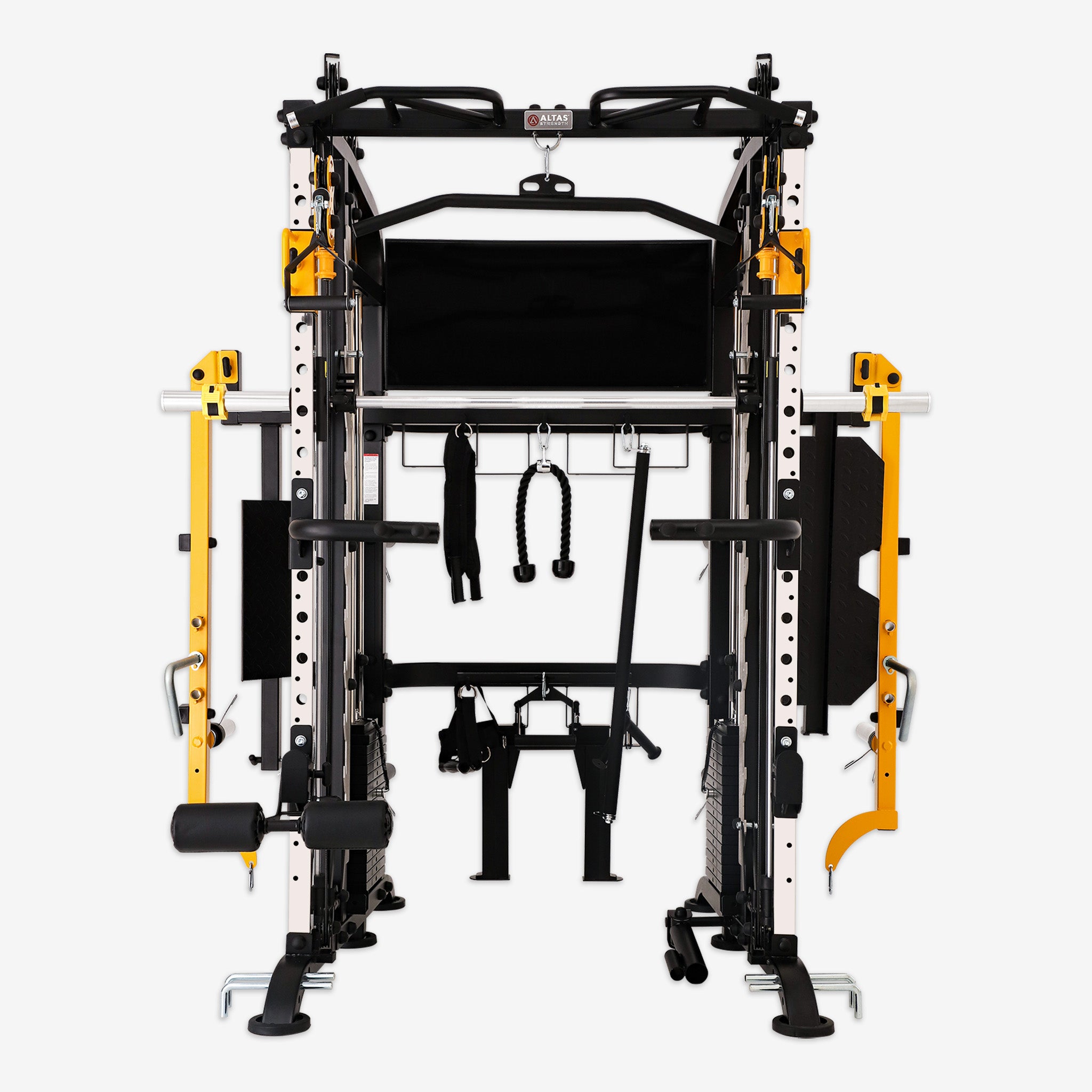
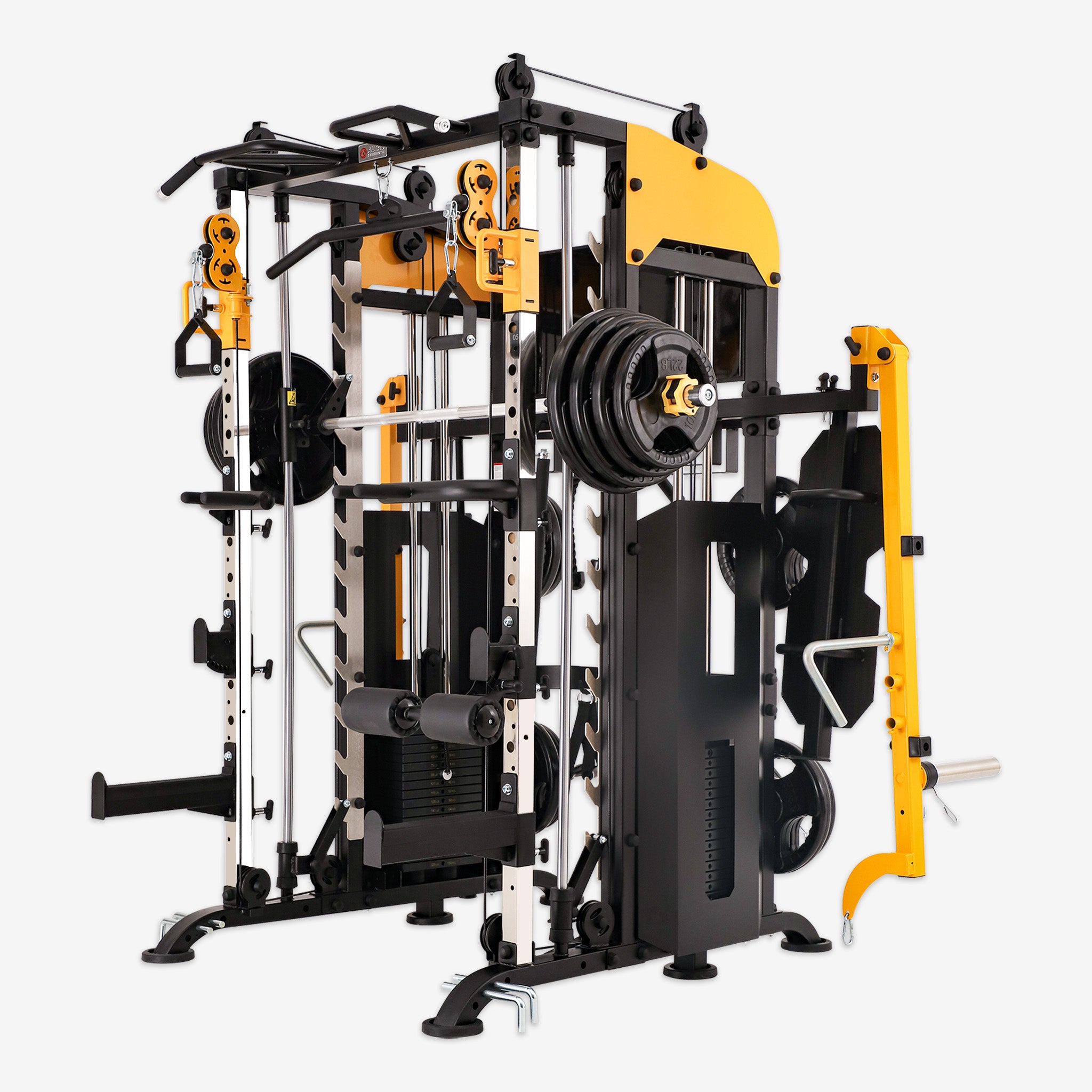
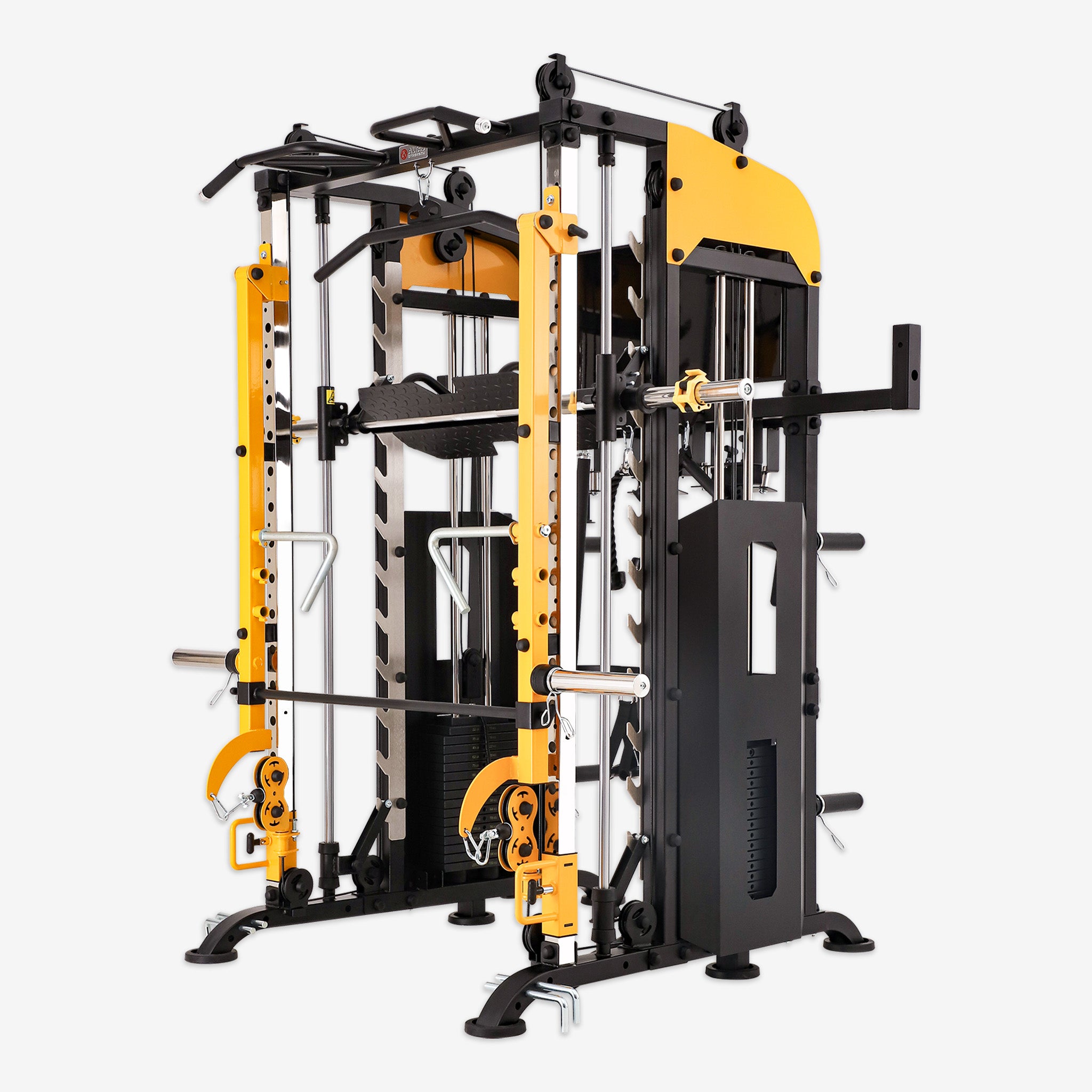
In the fitness world, squats hold a place of importance as a foundational exercise for building strength, enhancing muscle tone, and improving explosive power. However, for beginners or those still refining their technique, performing free squats may pose some safety challenges. The Smith machine offers a safe and supportive environment for learning and mastering squats.
I. Advantages of Smith Machine Squats
1. Enhanced Safety
- The Smith machine’s fixed barbell path minimizes the risk of accidental injury, making it ideal for beginners.
- With its secure design, beginners can train independently, reducing injury risks.
2. Posture Correction
- The fixed bar path assists users in learning correct squat form, reducing incorrect movements.
- Those refining their squat technique benefit from repeated practice, gradually perfecting their form.
3. Ease of Adjustment
- The Smith machine provides height and safety adjustments to suit each user’s body type and goals.
- Suitable for different heights, ensuring ideal bar placement every time.
4. Weight Stability
- A stable bar path instills confidence when lifting heavy weights, allowing users to safely push their limits.
- This stability encourages increased training intensity, facilitating faster muscle growth and strength gains.
5. Versatility
- Besides back squats, the Smith machine supports variations like front and narrow-stance squats, diversifying workouts.
- Suitable for all fitness levels, from beginners to advanced trainers.
II. Technical Aspects of Smith Machine Squats
1. Proper Stance
- Stand centered, feet shoulder-width apart, with toes slightly outward.
- Position the bar at shoulder height, adjusting as needed for comfortable alignment.
2. Grip on the Bar
- Use a grip slightly wider than shoulder-width, keeping hands evenly placed.
3. Squatting Process
- Keep your back straight, core engaged, and gaze forward.
- Slowly lower yourself until thighs are parallel to the ground, maintaining knee alignment with toes.
4. Rising Process
- Push through heels to rise, maintaining body stability throughout the movement.
- Avoid sudden rises to prevent joint strain.
5. Breathing Techniques
- Inhale on the descent, exhale on the rise, maintaining steady breath control.
III. Precautions for Smith Machine Squats
1. Avoid Over-Reliance
- Excessive reliance on the Smith machine may reduce balance and flexibility. Transition to free squats over time for better athletic performance.
2. Avoid Overloading
- Start with lighter weights, gradually increasing load to prevent muscle and joint strain.
3. Joint Health
- Squats can strain knees and ankles. Warm up thoroughly and maintain a safe range of motion.
4. Supplementary Training
- Complement squats with exercises like deadlifts and bench presses to enhance overall fitness and avoid muscle imbalances.
5. Continuous Learning
- Regularly refer to training guides and tutorials to ensure correct form and prevent bad habits from forming.
Conclusion
Smith machine squats provide a safe and effective way for fitness enthusiasts to incorporate squats into their workout routine. With proper technique and mindful practice, users can achieve their fitness goals and reduce the risk of injury. Over time, transitioning to free squats is advisable as experience and confidence grow. Regardless of your chosen method, a consistent and scientifically sound training plan will lead to success.