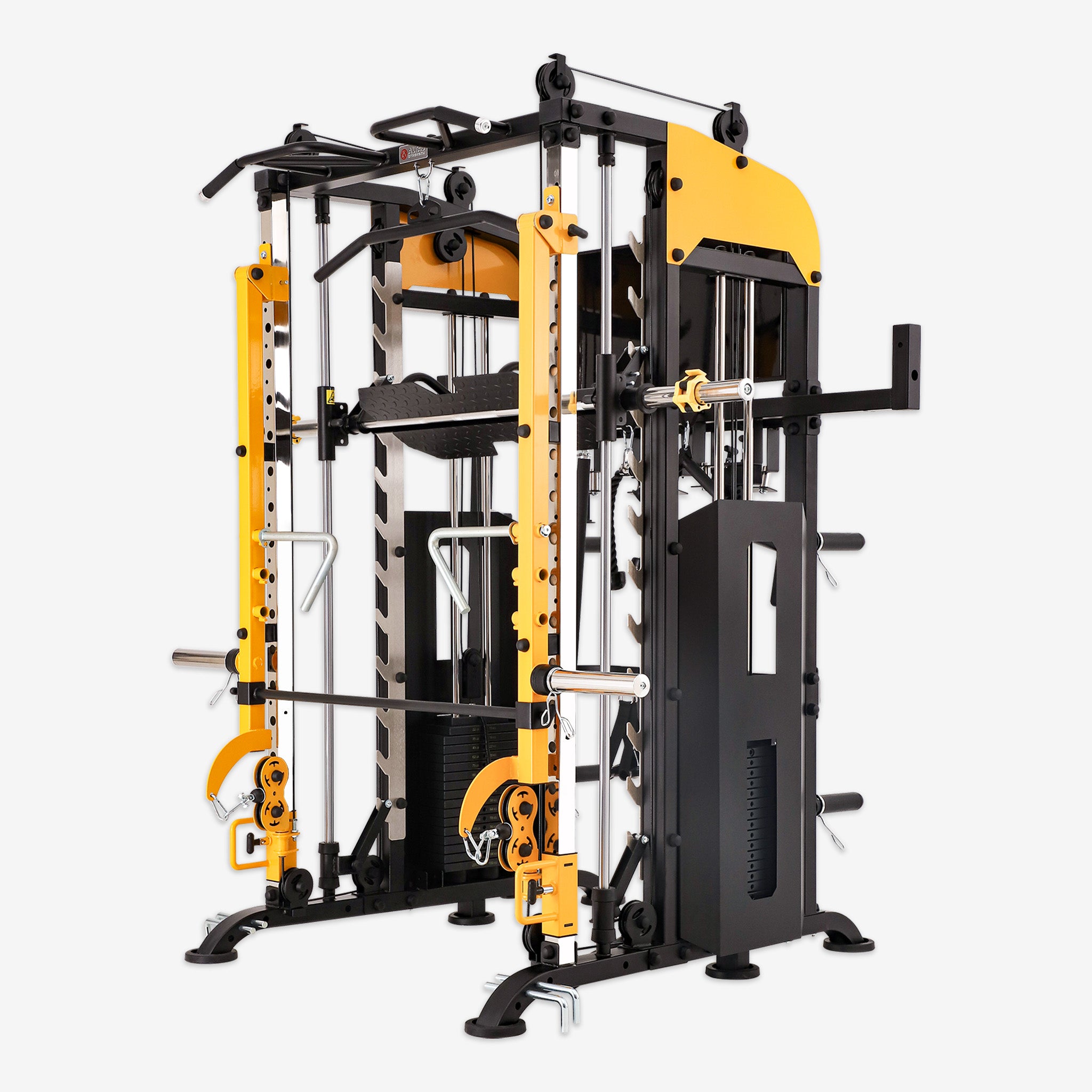
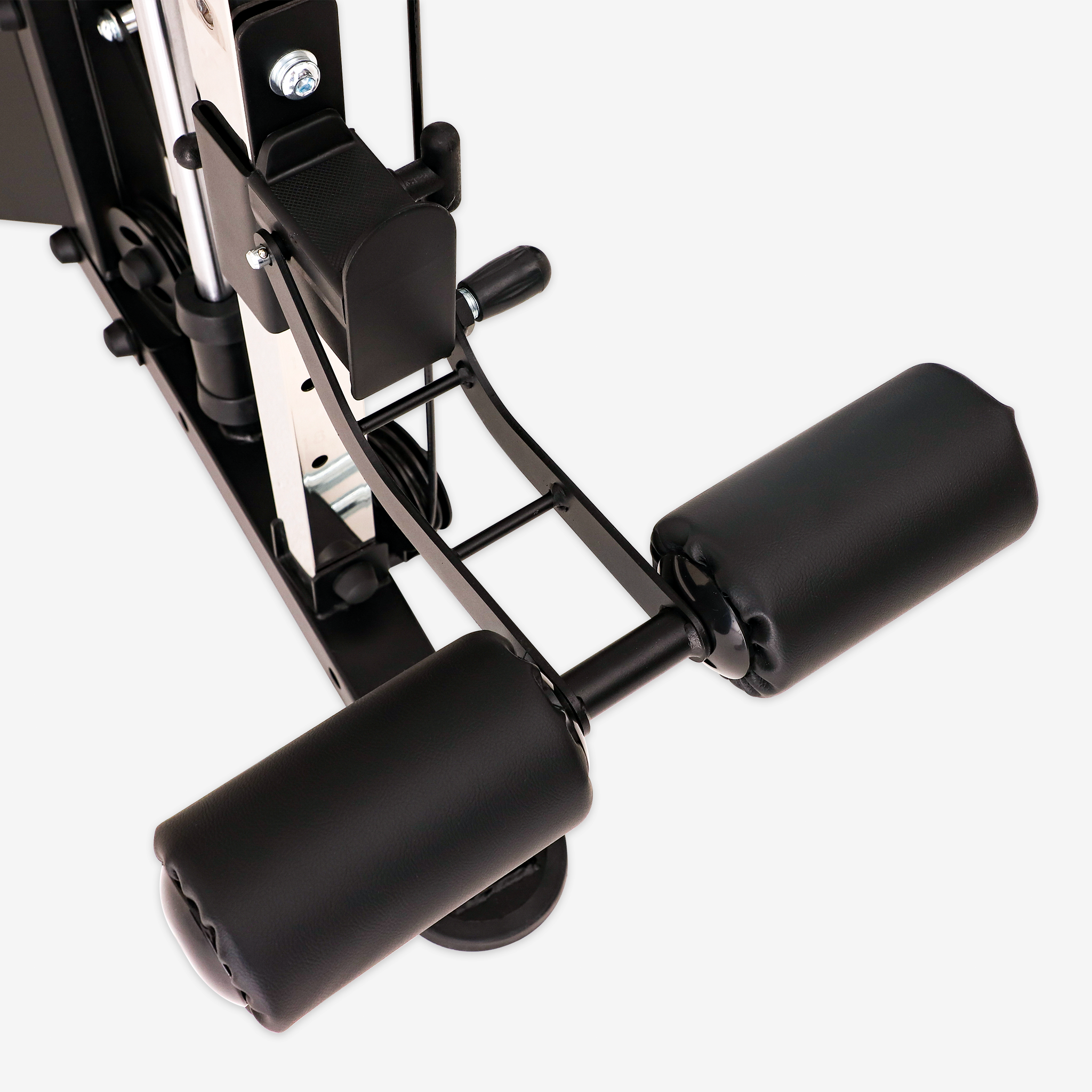
Introduction
Leg curls are a fundamental exercise for strengthening the hamstrings, glutes, and calves. As a crucial component of lower-body training, they enhance athletic performance, reduce injury risk, and improve overall muscle balance. Whether you are a professional athlete or a fitness enthusiast, incorporating leg curls into your routine can lead to significant benefits.
I. Strengthening the Posterior Chain for Optimal Performance
Leg curls primarily target the hamstrings and glutes while engaging the calf muscles as stabilizers. This strengthens the posterior chain, which is essential for powerful movements like sprinting, jumping, and squatting. Studies have shown that hamstring development improves stride efficiency and explosive power, making leg curls a valuable exercise for athletes.
Additionally, strong hamstrings support hip extension, enhancing performance in compound movements such as deadlifts. By incorporating leg curls, you can achieve greater stability and power in lower-body exercises.
II. Injury Prevention and Rehabilitation
One of the key benefits of leg curls is their ability to reduce the risk of injuries, especially in the knees and hamstrings. The controlled movement minimizes stress on the joints, making it an ideal exercise for individuals recovering from knee injuries. Strengthening the hamstrings helps balance the force exerted by the quadriceps, reducing the likelihood of anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries.
For rehabilitation, leg curls provide a safe and effective way to rebuild strength and stability. The machine-assisted variation offers controlled resistance, allowing for gradual progression in strength recovery.
III. Enhancing Muscle Definition and Aesthetics
Leg curls contribute to well-defined and proportional lower-body muscles. By targeting the hamstrings and glutes, they help create a balanced physique.
-
Low weight, high reps: Improves muscle endurance and definition.
-
Heavy weight, low reps: Promotes muscle hypertrophy and strength gains.
A well-developed posterior chain complements quadriceps growth, preventing muscle imbalances and improving overall symmetry.
IV. Versatile Training Variations
Leg curls can be performed in various ways to suit different training levels and environments:
-
Seated or lying leg curl machine – Ideal for beginners, providing stable support.
-
Nordic leg curls – Advanced bodyweight variation emphasizing eccentric control.
-
Dumbbell leg curls – Home-friendly option using free weights.
-
Resistance band leg curls – Portable and adaptable for different resistance levels.
-
Unilateral training – Corrects muscle imbalances by isolating each leg.
V. Key Considerations for Effective Training
To maximize the benefits of leg curls, consider these essential tips:
-
Maintain proper form – Avoid using momentum and focus on controlled movements.
-
Choose the right weight – Use a challenging yet manageable load to prevent compensatory movements.
-
Protect your joints – Modify the range of motion if you have knee concerns.
-
Incorporate complementary exercises – Combine leg curls with squats, deadlifts, and lunges for a well-rounded lower-body workout.
Conclusion
Leg curls are an essential exercise for strengthening the posterior chain, preventing injuries, and enhancing overall lower-body function. Whether your goal is athletic performance, muscle definition, or rehabilitation, incorporating leg curls into your training program can provide lasting benefits. Prioritize proper technique and progressive overload to maximize your results.